What is Blockchain Technology: Know Its Use Cases And Importance

Blockchain technology underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but its applications extend far beyond. It functions as a secure, decentralised database shared across a network of computers. Blockchain technology goes beyond just cryptocurrencies. Imagine a shared, digital ledger that's constantly being updated and replicated across a vast network of computers. This is essentially what blockchain is. Transactions are grouped into blocks, securely linked together, and chronologically ordered. This tamper-proof system offers increased transparency and security for recording any digital asset, be it financial transactions, medical data, or even intellectual property. The potential applications of blockchain technology continue to evolve, making it a disruptive force in various industries.
Key Takeaways
Blockchain is one type of database that is different from the typical database that stores information linked in blocks through cryptography.
One of the most common uses of transactions is through a ledger.
The data stored in the blockchain is irreversible as it is permanently recorded.
Importance of Blockchain

Every business runs on information. The faster it is received, the greater the accuracy associated with it. Blockchain is ideal for delivering information because it provides immediate, shared, and transparent details that are stored on the immutable ledger, which can be accessed with the permission of network members. A blockchain network can help track orders, payments, accounts, production, and many more things that are associated with it.
Key elements of a blockchain
Distributed ledger technology:
All the participants in the network have access to the distributed ledger with immutable records of transactions. The shared ledger, transactions, and elimination of duplication are available with this technology.
Immutable records:
No participant can change or tamper with the transaction after it is recorded in the shared ledger. If a transaction record involves an error, a new transaction is added to reverse the error, where both transactions are visible.
Smart Contracts:
To speed up the transactions, there is a set of rules called a smart contract. It is stored on the blockchain, which is executed automatically. A smart contract can define the conditions of corporate bond transfers, which include the terms for travel insurance that can be paid and many other things.
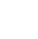
How does blockchain work?
The working of blockchain involves a few steps, which are:
Blocks are interconnected:
The blocks from a chain of data are moved from one place to another. The block schedules a strict time and the sequence of transactions where blocks are securely linked together to prevent any block from being altered or a block being inserted between the two existing blocks.
Transaction in Blockchain:
Each additional block strengthens the verification of the previous block and the complete blockchain. It renders the blockchain tamper-evident, delivering the key strength of immutability. It also removes the possibility of tampering and builds a ledger of transactions with other network members that are trustworthy.
Verification:
The participating systems of computers are known as miners, which evaluate transactions through mathematical calculations that determine their validity. This helps in generating transparent verification of data that are free from biases and are helpful and is considered to be one of the crucial aspects of blockchain technology.
Hash:
Each verified block has a cryptographic hash that contains references to the previous ones. It provides security and stability for all the transactions happening. It also generates digital fingerprints which adds an extra layer of security which is an essential component.
Execution:
The value of money in a unit moves from one party to another. It is a pathway through which transactions are done. If one party initiates a transaction using a cryptocurrency wallet through an application that provides an interface. It has a designed sequence of events.
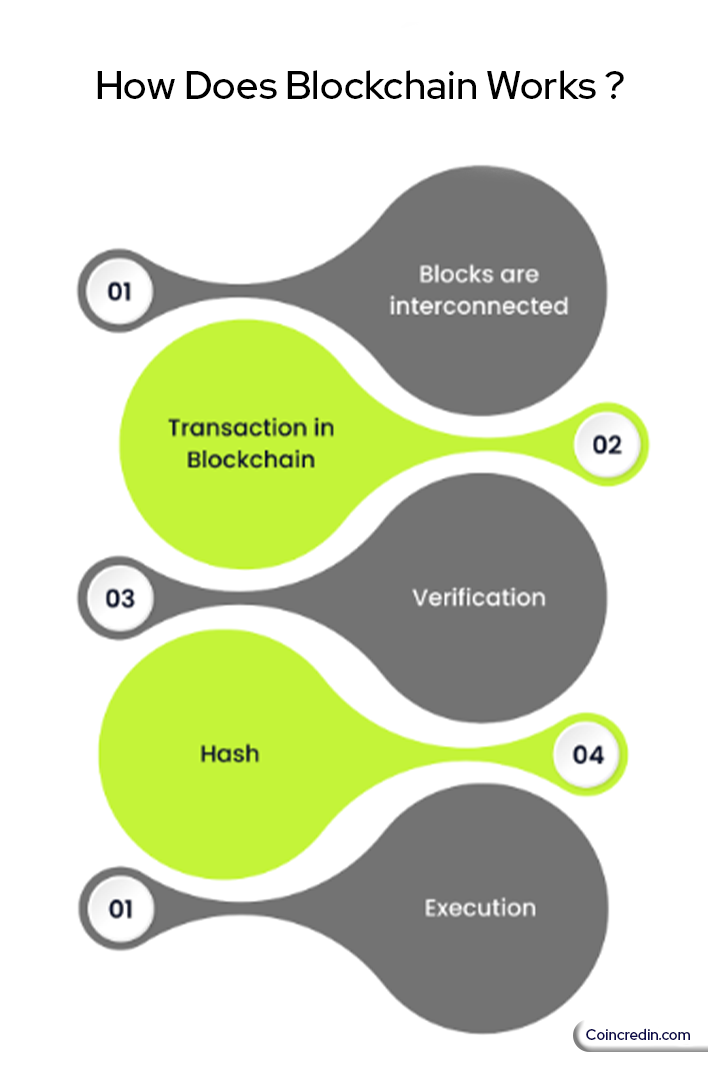
Types of blockchain network
Public Blockchain:
This is one of the first types of blockchain technology known as public blockchain. This pattern of blockchain has completely removed the issues that come with centralization, such as security and transparency. Distributed ledger technology does not store information in any one place; instead, it is distributed all across the peer-to-peer network. The decentralized nature needs some verification methods that assure the authenticity of the data. The method is a consensus algorithm where participants in the blockchain have reached agreements for the current state of the ledger. Proof of work or proof of stake are two common methods of consensus. It is non-restrictive and permissionless for anyone who has internet access and can sign up for the blockchain platform to become an authorized node. A user can access the current records to conduct mining activities. The complex computations are used to verify the transactions and add them to the ledger. There is no valid record or transaction that can be used to change the network and help verify the transactions that have bugs or propose changes because the source code is usually open source.
Advantages of the Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are completely independent of organisations, and they will continue to run as long as computers are connected. The networks are also transparent as long as the users follow the security protocols and methods, and nevertheless, public blockchains are mostly safe and secure.
Drawbacks of the Public Blockchain
The network can be slow, and companies cannot restrict its access or use. Hackers can gain 51% of the computing power of a public blockchain network, which can be unintendedly altered. One other disadvantage is that it does not scale well, and there is an issue with the network as it slows down when more nodes join the network.
Use cases of the Public Blockchain
The most common use case for public blockchain mining is exchanging cryptocurrencies through the platform. It can also be created for fixing a record with an audible chain of custody, like electronic notarization and public records of property ownership. This type of blockchain is ideal for organisations that are built on transparency, like social support groups and non-government organisations.
Private Blockchain
A blockchain network works in a restrictive environment, which is a closed network under the control of a single entity, which is a private blockchain. The private blockchain is on a smaller scale. Private blockchains are typically operated on the small network of a company or organisation.
Advantages of the Private Blockchain
The organisation has its own permission level, security, authorization, and accessibility. Private blockchains are limited in size, which can turn out to be very fast and can help process transactions, which is much quicker than any public blockchain.
Disadvantages of the Private Blockchain
Private blockchain includes controversial claims, as the core philosophy of any blockchain is decentralisation. It is very difficult to completely achieve trust in the information, as centralised notes work on validity. The small number of nodes also means less security. The source code of a private blockchain is proprietary and closed. Users cannot independently audit or confirm it, which can lead to less security.
Use cases of the Private Blockchain
The speed of private blockchain makes it ideal for cases where blockchain needs to be cryptographically secure but the controlling entity does not want the information to be accessed by the public.
Hybrid Blockchain
A type of blockchain that has a combination of private and public blockchains It allows an organisation to set up a private, permission-based system with a public, permissionless system. It allows them to control where one can access specific data that is stored in the blockchain. Records and transactions made in a hybrid blockchain are not accessible to the public, but records can be verified whenever they are needed. Confidential information is kept inside the network, which can also be verified. No alteration of transactions is allowed in a hybrid blockchain. When a user joins a hybrid blockchain, it has full access to the network. The user's identity is protected from other users unless they engage in transactions.
Advantages of the Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchain works within a closed ecosystem. The outside hackers cannot mount a 51% attack on the network. The transactions are cheap, fast, and offer scalability compared to any public blockchain network.
Disadvantages of the Hybrid Blockchain
The type of blockchain is not completely transparent because the information is not protected.
Use cases of the Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchain has various strong use cases, including real estate. Companies can use a hybrid blockchain, which runs the system privately and reflects certain information, like listings, to the public. Retail can also streamline the process with hybrid blockchain, which is a highly regulated market.
Consortium Blockchain
The fourth type of blockchain is also called federated blockchain. It also holds features of public and private blockchain but is dissimilar in that multiple organisation members collaborate for a decentralised network. A consortium blockchain is a private blockchain that limits the access of a particular group, which eliminates the risk that comes with having one entity control the network on a private blockchain.
Advantages of consortium blockchain
This blockchain is more secure, safe, scalable, and efficient than a public blockchain network. It also offers access controls.
Disadvantages of consortium blockchain
The consortium blockchain is less transparent than any public blockchain. It can only be compromised if any member node is breached. Blockchain regulations can impair network functionality.
Use cases of consortium blockchain
Banking and payments are used in this type of blockchain. The different banks can band together and form a consortium, which decides the validity of transactions. Research organisations can create a similar model where organisations can track food. It is ideal for supply chains in food and medicine applications.
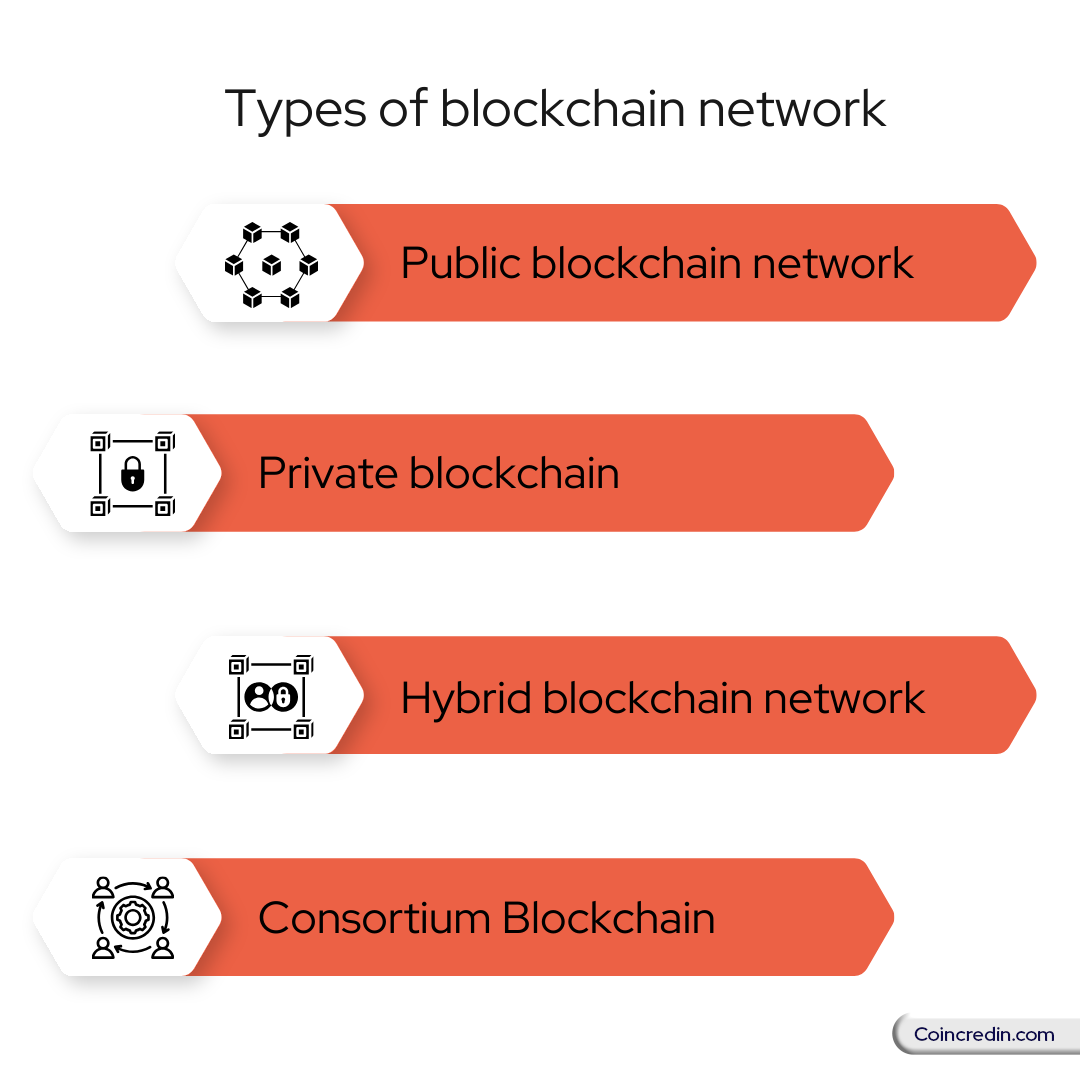
Use of blockchain in different industries
Blockchain is an emerging technology that is being adopted in innovative ways by different industries. Some industries are:
Energy
Finance
Media and Entertainment
Retail
Energy:
The companies associated with energy create peer-to-peer energy trading platforms and streamline their access to renewable energy, like selling electricity between individuals. Homeowners who have installed solar panels use the platform to sell their excess solar energy to neighbours. This process is automated with smart meters, which create transactions and blockchain records them. Users also sponsor solar panels in areas where there is a shortage of energy.
Finance:
Financial systems like banks and stock exchanges use the services of blockchain to manage online payments, market trading, and accounts.
Media and Entertainment:
The technology of blockchain is used in the company of media and entertainment, which manages the copyright data. The fair compensation of artists depends on copyright verification, which is critical. Multiple transactions record the sale or transfer of copyright content.
Retail:
Retail companies use blockchain to track the movement of goods between two parties, which are buyers and sellers.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology seems to be setting high standards in terms of innovation and invention. That being said, it is for the same reason that its acceptance is being recognised by almost all major industries. Industries are getting comfortable with the idea of agreeing with a publicly distributed ledger in their daily business, because of the security it guarantees.
Some of the central banks of big economies of the world, like the US, the UK, India, and many others are reflecting positive acceptance towards cryptocurrency and are joining hands to launch digital coins which reflects the success that platforms based on blockchain technology will achieve in the coming times.
Written by: Suhani Jain